Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Saito, Takumi*; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Okubo, Takahiro*; Miura, Daisuke*; Kumada, Takayuki
Environmental Science & Technology, 57(26), p.9802 - 9810, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Engineering, Environmental)
 -, SeO
-, SeO
 -, and SeO
-, and SeO
 -coprecipitated barite after treatment with phosphate
-coprecipitated barite after treatment with phosphateTokunaga, Kohei; Tanaka, Kazuya; Takahashi, Yoshio*; Kozai, Naofumi
Environmental Science & Technology, 57(8), p.3166 - 3175, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:46.42(Engineering, Environmental)Coprecipitation of radionuclides with barite has been studied to remove radionuclides from radioactive liquid waste because of its excellent removal efficiency; however, little information exists concerning the stability of the ions coprecipitated with barite. This study systematically investigated the stability of iodate, selenite, and selenate coprecipitated with barite via leaching tests. These oxyanions were gradually leached from the oxyanion-bearing barite into ultrapure water over time. Leaching of the oxyanions significantly increased in leaching solutions containing NaCl (pH5.3), NaNO (pH5.9), and Na
(pH5.9), and Na SO
SO (pH5.7). Conversely, leaching of the oxyanions was suppressed in KH
(pH5.7). Conversely, leaching of the oxyanions was suppressed in KH PO
PO solution (pH8.5), indicating that phosphate stabilized the oxyanion-bearing barite. The effect of phosphate treatment on oxyanion-bearing barite was further investigated. The results showed that the barite surface was modified with phosphate, and a thin surface layer of a barium phosphate-like structure was formed. The amount of oxyanions leached from the phosphate-treated samples into leaching solutions containing NaCl or NaNO
solution (pH8.5), indicating that phosphate stabilized the oxyanion-bearing barite. The effect of phosphate treatment on oxyanion-bearing barite was further investigated. The results showed that the barite surface was modified with phosphate, and a thin surface layer of a barium phosphate-like structure was formed. The amount of oxyanions leached from the phosphate-treated samples into leaching solutions containing NaCl or NaNO was much lower than the amounts leached from the untreated barite samples into ultrapure water. The barite coprecipitation combined with subsequent phosphate treatment may be a promising method to efficiently remove iodate, selenite, and selenate from wastewater and stabilize them as barite coprecipitates.
was much lower than the amounts leached from the untreated barite samples into ultrapure water. The barite coprecipitation combined with subsequent phosphate treatment may be a promising method to efficiently remove iodate, selenite, and selenate from wastewater and stabilize them as barite coprecipitates.
Kaneyasu, Naoki*; Kutsuna, Shuzo*; Iida, Kenjiro*; Sanada, Yukihisa; Tajiri, Takuya*
Environmental Science & Technology, 56(17), p.12036 - 12044, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Engineering, Environmental)Radionuclides released during the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear accident caused altitude-dependent surface contamination in the mountainous areas of Japan. To explore the possible cloudwater deposition that formed a distinctive contamination profile, data from pollen sensors deployed nationwide were analyzed. Utilizing the polarization of scattered light, Cedar pollen and water droplets were distinguished. On March 15, when surface contamination was simulated in previous studies, dense cloud with high droplet number density were observed outside the  Cs surface deposition areas, indicating that the sensor sites were immersed amid cloud layers. In contrast, cloud droplets with moderate number density were measured at altitudes of approximately 570-840 m, which overlapped with the surface contamination areas. Considering the existing knowledge on vertical gradients of cloudwater composition, these suggest that contaminated cloud droplets were localized near the cloud base where a moderate number density of cloud droplets was measured. A formation process was proposed for the observed vertical distribution, that is, surface contamination occurred intensively at the contact line between the cloud base and mountain slopes via cloudwater deposition, and the descending cloud base formed the contamination zone. This study sheds light on the deposition processes of radionuclides which have not previously been clarified.
Cs surface deposition areas, indicating that the sensor sites were immersed amid cloud layers. In contrast, cloud droplets with moderate number density were measured at altitudes of approximately 570-840 m, which overlapped with the surface contamination areas. Considering the existing knowledge on vertical gradients of cloudwater composition, these suggest that contaminated cloud droplets were localized near the cloud base where a moderate number density of cloud droplets was measured. A formation process was proposed for the observed vertical distribution, that is, surface contamination occurred intensively at the contact line between the cloud base and mountain slopes via cloudwater deposition, and the descending cloud base formed the contamination zone. This study sheds light on the deposition processes of radionuclides which have not previously been clarified.
Francisco, P. C. M.; Matsumura, Daiju; Kikuchi, Ryosuke*; Ishidera, Takamitsu; Tachi, Yukio
Environmental Science & Technology, 56(5), p.3011 - 3020, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:27.6(Engineering, Environmental) and Tb
and Tb measured by gel electrophoresis techniques
measured by gel electrophoresis techniquesNakano, Sumika*; Marumo, Kazuki*; Kazami, Rintaro*; Saito, Takumi*; Haraga, Tomoko; Tasaki-Handa, Yuiko*; Saito, Shingo*
Environmental Science & Technology, 55(22), p.15172 - 15180, 2021/11
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:33.8(Engineering, Environmental)Humic acid (HA) can strongly complex with metal ions to form a supramolecular assembly via coordination binding. However, determining the supramolecular size distribution and stoichiometry between small HA unit molecules constituting HA supramolecule and metal ions has proven to be challenging. Here, we investigated the changes in the size distributions of HAs induced by Cu and Tb
and Tb ions using a unique polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) for the separation and quantification of HA complexes and metal ions bound, followed by UV-Vis spectroscopy and EEM-PARAFAC. It was found that the supramolecular behaviors of Cu
ions using a unique polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) for the separation and quantification of HA complexes and metal ions bound, followed by UV-Vis spectroscopy and EEM-PARAFAC. It was found that the supramolecular behaviors of Cu and Tb
and Tb complexes with HA collected from peat and deep groundwater (HHA) differed. Our results suggest that this supramolecular stoichiometry is related to the abundance of sulfur atoms in the elemental composition of HHA. Our results provide new insights into HA supramolecules formed via metal complexation.
complexes with HA collected from peat and deep groundwater (HHA) differed. Our results suggest that this supramolecular stoichiometry is related to the abundance of sulfur atoms in the elemental composition of HHA. Our results provide new insights into HA supramolecules formed via metal complexation.
Taniguchi, Keisuke*; Onda, Yuichi*; Smith, H. G.*; Blake, W.*; Yoshimura, Kazuya; Yamashiki, Yosuke*; Kuramoto, Takayuki*; Saito, Kimiaki
Environmental Science & Technology, 55(13), P. 9394, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.24(Engineering, Environmental)no abstracts in English
Otosaka, Shigeyoshi*; Kambayashi, Shota*; Fukuda, Miho*; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Misono, Toshiharu; Suzuki, Takashi; Aono, Tatsuo*
Environmental Science & Technology, 54(21), p.13778 - 13785, 2020/11
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:53.03(Engineering, Environmental)Concentrations of  Cs in seawater, seabed sediment, and pore water collected from the area around Fukushima were investigated from 2015 to 2018, and the potential of coastal sediments to supply radiocesium to the bottom environment was evaluated. The
Cs in seawater, seabed sediment, and pore water collected from the area around Fukushima were investigated from 2015 to 2018, and the potential of coastal sediments to supply radiocesium to the bottom environment was evaluated. The  Cs concentration in the pore water ranged from 33 to 1934 mBq L
Cs concentration in the pore water ranged from 33 to 1934 mBq L and was 10-40 times higher than that in the overlying water (seawater overlying within 30 cm on the seabed). At most stations, the
and was 10-40 times higher than that in the overlying water (seawater overlying within 30 cm on the seabed). At most stations, the  Cs concentrations in the overlying water and the pore water were approximately proportional to those in the sediment. The conditional partition coefficient between pore water and sediment was 0.9-14
Cs concentrations in the overlying water and the pore water were approximately proportional to those in the sediment. The conditional partition coefficient between pore water and sediment was 0.9-14 10
10 L kg
L kg , independent of the year of sampling. These results indicated that an equilibrium of
, independent of the year of sampling. These results indicated that an equilibrium of  Cs between pore water and sediment has established in a relatively short period, and
Cs between pore water and sediment has established in a relatively short period, and  Cs in the pore water is gradually exported to seawater near the seabed. A simple box model estimation based on these results showed that the
Cs in the pore water is gradually exported to seawater near the seabed. A simple box model estimation based on these results showed that the  Cs in the sediment was decreased by about 6% per year by desorption/diffusion of
Cs in the sediment was decreased by about 6% per year by desorption/diffusion of  Cs from the seabed.
Cs from the seabed.
 -humate complexes
-humate complexesMarumo, Kazuki*; Matsumoto, Atsumasa*; Nakano, Sumika*; Shibukawa, Masami*; Saito, Takumi*; Haraga, Tomoko; Saito, Shingo*
Environmental Science & Technology, 53(24), p.14507 - 14515, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:28.45(Engineering, Environmental)Humic acids (HA) are responsible for the fate of metal ions in the environment. We developed a polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) technique to investigate the MW distributions of metal ion (copper ion). Combining contaminant-metal-free and high-resolution PAGE systems for HA provided accurate MW distributions for the metal ions. Coupling this system with UV-Vis spectrometry and the excitation-emission matrix (EEM) spectrometry-parallel factor analysis (PARAFAC) method revealed new insights into metal-HA complex. Interestingly, the MW distributions of the three metal ions were entirely different, indicating that the presence of specific binding environments in HA for the metal ions depending its MW. The MW distributions of five fluorescent components were associated with the metal ion distributions. Our PAGE-based methodology suggests that metal binding sites and fluorescent components in HA exhibit heterogeneity in terms of metal binding affinity and MW.
Taniguchi, Keisuke*; Onda, Yuichi*; Smith, H. G.*; Blake, W.*; Yoshimura, Kazuya; Yamashiki, Yosuke*; Kuramoto, Takayuki*; Saito, Kimiaki
Environmental Science & Technology, 53(21), p.12339 - 12347, 2019/11
Times Cited Count:75 Percentile:95.09(Engineering, Environmental)Wu, H.*; Wang, Y.*; Ikeda, Atsushi; Miller, C. J.*; Waite, T. D.*
Environmental Science; Water Research & Technology, 5(8), p.1400 - 1411, 2019/08
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:32.59(Engineering, Environmental)In this study, the distributions of iron and phosphorus species in a 1.25 m pilot scale submerged membrane bioreactor dosed with Fe(II) salts to either the membrane chamber or the 1st anoxic chamber were determined using X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) at the iron and phosphorus K-edges. Significant differences in the distribution of Fe species were evident at the commencement of dosing depending on the chamber to which Fe(II) was dosed though these differences were much less distinct by the time steady state conditions were achieved. Both the co-precipitation of P with Fe and adsorption of phosphorus to iron oxides play important roles with regard to the removal of phosphorus from the MBR supernatant with the results of this work suggesting that P removal via formation of Fe(III)-phosphate mineral species is preferred if Fe(II) is dosed to the membrane chamber rather than the 1st anoxic chamber.
pilot scale submerged membrane bioreactor dosed with Fe(II) salts to either the membrane chamber or the 1st anoxic chamber were determined using X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) at the iron and phosphorus K-edges. Significant differences in the distribution of Fe species were evident at the commencement of dosing depending on the chamber to which Fe(II) was dosed though these differences were much less distinct by the time steady state conditions were achieved. Both the co-precipitation of P with Fe and adsorption of phosphorus to iron oxides play important roles with regard to the removal of phosphorus from the MBR supernatant with the results of this work suggesting that P removal via formation of Fe(III)-phosphate mineral species is preferred if Fe(II) is dosed to the membrane chamber rather than the 1st anoxic chamber.
 Sr in fallout particles collected in the difficult-to-return zone around the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant
Sr in fallout particles collected in the difficult-to-return zone around the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power PlantZhang, Z.*; Igarashi, Junya*; Satou, Yukihiko; Ninomiya, Kazuhiko*; Sueki, Keisuke*; Shinohara, Atsushi*
Environmental Science & Technology, 53(10), p.5868 - 5876, 2019/05
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:62.74(Engineering, Environmental)The Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNPP) accident released abundant radioactive particles into the surrounding environment. Herein, we analyzed the activity of  Sr in these particles to estimate the contribution of this radionuclide to the overall radiation exposure and shed light on the processes that occurred during the accident. Seven radioactive particles were isolated from the dust and soil samples collected from areas surrounding the FDNPP, and the minimum/maximum
Sr in these particles to estimate the contribution of this radionuclide to the overall radiation exposure and shed light on the processes that occurred during the accident. Seven radioactive particles were isolated from the dust and soil samples collected from areas surrounding the FDNPP, and the minimum/maximum  Cs activities were determined as 224/4,100 Bq. Based on the size, specific activity, and
Cs activities were determined as 224/4,100 Bq. Based on the size, specific activity, and  Cs/
Cs/ Cs activity ratios, we concluded that six of the seven radioactive particles were released from the Unit 1 reactor, while one particle was released from the Unit 3 reactor by a hydrogen explosion. Strontium-90 was detected in all radioactive particles, and the minimal/maximal
Cs activity ratios, we concluded that six of the seven radioactive particles were released from the Unit 1 reactor, while one particle was released from the Unit 3 reactor by a hydrogen explosion. Strontium-90 was detected in all radioactive particles, and the minimal/maximal  Sr activities were determined as 0.046/1.4 Bq.
Sr activities were determined as 0.046/1.4 Bq.  Cs/
Cs/ Sr activity ratios above 1000 were observed for all seven particles, that is, compared to
Sr activity ratios above 1000 were observed for all seven particles, that is, compared to  Cs,
Cs,  Sr had negligible contribution to the overall radiation exposure. The
Sr had negligible contribution to the overall radiation exposure. The  Cs/
Cs/ Sr activity ratios of the radioactive particles were similar to those of terrestrial environmental samples and were higher for particles released from the Unit 1 reactor than for samples collected from the Unit 1 reactor building, which indicates possibility of additional
Sr activity ratios of the radioactive particles were similar to those of terrestrial environmental samples and were higher for particles released from the Unit 1 reactor than for samples collected from the Unit 1 reactor building, which indicates possibility of additional  Sr -rich contamination after release of the particles.
Sr -rich contamination after release of the particles.
 -CO
-CO ternary complex from brackish potable groundwater; Complex dissociation, transport, and sorption
ternary complex from brackish potable groundwater; Complex dissociation, transport, and sorptionMa, J.*; Zhang, Y.*; Collins, R. N.*; Tsarev, S.*; Aoyagi, Noboru; Kinsela, A. S.*; Jones, A. M.*; Waite, T. D.*
Environmental Science & Technology, 53(5), p.2739 - 2747, 2019/03
Times Cited Count:47 Percentile:89.02(Engineering, Environmental)Tokunaga, Kohei*; Takahashi, Yoshio*
Environmental Science & Technology, 51(16), p.9194 - 9201, 2017/08
Times Cited Count:46 Percentile:82.67(Engineering, Environmental)In the present study, we explore a new application of barite (BaSO ) as a sequestering phase for selenite (Se(IV)) and selenate (Se(VI)) ions from aqueous solutions due to the low solubility and high stability of barite. The uptake of Se(IV) and Se(VI) during coprecipitation with barite was investigated through batch experiments to understand the factors controlling effective removal of Se(IV) and Se(VI) from polluted water to barite. The uptake of Se(IV) by barite is dependent on pH, coexistent calcium ion, and sulfate concentration in the initial solution, possibly due to their effects on the chemical affinity and structural similarity. On the other hand, the uptake of Se(VI) by barite was strongly dependent on sulfate concentration in the initial solution, which is only related to the structural similarity. This study provides a good estimate of its ability to effectively remove Se(IV) and Se(VI) from aqueous solutions (more than 80%) under optimized experimental parameters.
) as a sequestering phase for selenite (Se(IV)) and selenate (Se(VI)) ions from aqueous solutions due to the low solubility and high stability of barite. The uptake of Se(IV) and Se(VI) during coprecipitation with barite was investigated through batch experiments to understand the factors controlling effective removal of Se(IV) and Se(VI) from polluted water to barite. The uptake of Se(IV) by barite is dependent on pH, coexistent calcium ion, and sulfate concentration in the initial solution, possibly due to their effects on the chemical affinity and structural similarity. On the other hand, the uptake of Se(VI) by barite was strongly dependent on sulfate concentration in the initial solution, which is only related to the structural similarity. This study provides a good estimate of its ability to effectively remove Se(IV) and Se(VI) from aqueous solutions (more than 80%) under optimized experimental parameters.
 Cs concentration in particles discharged from rice paddies to freshwater bodies after the Fukushima Daiichi NPP accident
Cs concentration in particles discharged from rice paddies to freshwater bodies after the Fukushima Daiichi NPP accidentYoshimura, Kazuya; Onda, Yuichi*; Wakahara, Taeko*
Environmental Science & Technology, 50(8), p.4186 - 4193, 2016/04
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:57.71(Engineering, Environmental)Buesseler, K. O.*; German, C. R.*; Honda, Makio*; Otosaka, Shigeyoshi; Black, E. E.*; Kawakami, Hajime*; Manganini, S. M.*; Pike, S.*
Environmental Science & Technology, 49(16), p.9807 - 9816, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:55.54(Engineering, Environmental)A three year time-series of particle fluxes is presented from sediment traps deployed at 500 and 1000 m at a site 115 km southeast of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNPP). Results show a high fraction of lithogenic material, suggesting a lateral source of sediments. The accident-derived radiocesium were enhanced in flux peaks that, given variations in trap  Cs/
Cs/ Pb ratios, are characteristic of material derived from shelf and slope sediments found from
Pb ratios, are characteristic of material derived from shelf and slope sediments found from  120 to
120 to  500 m. The fluxes of radiocesium are an order of magnitude higher than a previously reported for the trap located 100 km due east of FDNPP. We attribute the large difference due to the position of our trap under the southeasterly currents that carry contaminated waters and resuspended sediments in to the Pacific. These higher sedimentary fluxes of radiocesium to the offshore are still small relative to the inventory of radiocesium currently buried nearshore.
500 m. The fluxes of radiocesium are an order of magnitude higher than a previously reported for the trap located 100 km due east of FDNPP. We attribute the large difference due to the position of our trap under the southeasterly currents that carry contaminated waters and resuspended sediments in to the Pacific. These higher sedimentary fluxes of radiocesium to the offshore are still small relative to the inventory of radiocesium currently buried nearshore.
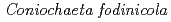
V zquez-Campos, X.*; Kinsela, A. S.*; Collins, R. N.*; Neilan, B. A.*; Aoyagi, Noboru; Waite, T. D.*
zquez-Campos, X.*; Kinsela, A. S.*; Collins, R. N.*; Neilan, B. A.*; Aoyagi, Noboru; Waite, T. D.*
Environmental Science & Technology, 49(14), p.8487 - 8496, 2015/07
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:67.5(Engineering, Environmental)The uptake and binding of uranium by a moderately acidophilic fungus, 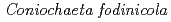 , recently isolated from a uranium mine site, is examined in this work in order to better understand the potential impact of organisms such as this on uranium sequestration in hydrometallurgical systems. Our results show that the viability of the fungal biomass is critical to their capacity to remove uranium from solution. Indeed, live biomass were capable of removing 16 mg U/g dry weight in contrast with dead biomass which removed 45 mg U/g dry weight after 2 h. Furthermore, the uranium binds with different strength, with a fraction ranging from 20-50 % being easily leachable from the exposed biomass by a 10 min acid washing. Results from X-ray absorption spectroscopy measurements show that the strength of uranium binding is strongly influenced by cell viability, with live cells showing a more well-ordered uranium bonding environment, while the distance to carbon or phosphorus second neighbours is similar in all samples. When coupled with laser spectroscopy, the importance of organic acids and phosphates, and polysaccharides, likely released with fungal cell death, appear to be the primary determinants of uranium binding in this system. These results provide an important progression to our understanding with regard to uranium sequestration in hydrometallurgical applications.
, recently isolated from a uranium mine site, is examined in this work in order to better understand the potential impact of organisms such as this on uranium sequestration in hydrometallurgical systems. Our results show that the viability of the fungal biomass is critical to their capacity to remove uranium from solution. Indeed, live biomass were capable of removing 16 mg U/g dry weight in contrast with dead biomass which removed 45 mg U/g dry weight after 2 h. Furthermore, the uranium binds with different strength, with a fraction ranging from 20-50 % being easily leachable from the exposed biomass by a 10 min acid washing. Results from X-ray absorption spectroscopy measurements show that the strength of uranium binding is strongly influenced by cell viability, with live cells showing a more well-ordered uranium bonding environment, while the distance to carbon or phosphorus second neighbours is similar in all samples. When coupled with laser spectroscopy, the importance of organic acids and phosphates, and polysaccharides, likely released with fungal cell death, appear to be the primary determinants of uranium binding in this system. These results provide an important progression to our understanding with regard to uranium sequestration in hydrometallurgical applications.
Mukai, Hiroki*; Hatta, Tamao*; Kitazawa, Hideaki*; Yamada, Hirohisa*; Yaita, Tsuyoshi; Kogure, Toshihiro*
Environmental Science & Technology, 48(22), p.13053 - 13059, 2014/12
Times Cited Count:113 Percentile:94.5(Engineering, Environmental)no abstracts in English
Otosaka, Shigeyoshi; Nakanishi, Takahiro; Suzuki, Takashi; Sato, Yuhi; Narita, Hisashi*
Environmental Science & Technology, 48(21), p.12595 - 12602, 2014/11
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:58.4(Engineering, Environmental)From August 2011 to July 2013, a sediment trap was deployed at 100 km east of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant and sinking particles were collected. Sinking flux of  Cs decreased over time with seasonal fluctuation. The
Cs decreased over time with seasonal fluctuation. The  Cs fluxes were mainly affected by two principal modes. One was a rapid sinking of radiocesium-bound particles (moderate mode). This mode was dominant especially in the early post-accident stage, and was presumed to establish the distribution of radiocesium in the offshore seabed. Another was the secondary transport of particles attributed to turbulence near the seabed and was observed in winter (turbulence mode). Although the latter process would not drastically change the distribution of sedimentary radiocesium, attention should be paid as this key process redistributing the accident-derived radiocesium may cumulatively affect the long-term distribution.
Cs fluxes were mainly affected by two principal modes. One was a rapid sinking of radiocesium-bound particles (moderate mode). This mode was dominant especially in the early post-accident stage, and was presumed to establish the distribution of radiocesium in the offshore seabed. Another was the secondary transport of particles attributed to turbulence near the seabed and was observed in winter (turbulence mode). Although the latter process would not drastically change the distribution of sedimentary radiocesium, attention should be paid as this key process redistributing the accident-derived radiocesium may cumulatively affect the long-term distribution.
Fukushi, Keisuke*; Hasegawa, Yusuke*; Maeda, Koshi*; Aoi, Yusuke*; Tamura, Akihiro*; Arai, Shoji*; Yamamoto, Yuhei*; Aosai, Daisuke*; Mizuno, Takashi
Environmental Science & Technology, 47(22), p.12811 - 12818, 2013/11
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:59.29(Engineering, Environmental)Eu(III) sorption on granite was examined by the combined microscopic and macroscopic approaches. Polished thin sections of the granite were reacted with solutions containing 10  M of Eu(III) and analyzed using EPMA and LA-ICP-MS. The Eu enrichment up to 6 wt.% was observed on most of the biotite grains. The Eu-enriched parts commonly lose K, which is the interlayer cation of biotite, indicating that the sorption mode is cation exchange in the interlayer. Batch Eu(III) sorption experiments on granite and biotite powders were conducted. The macroscopic sorption behavior of biotite was consistent with that of granite. The obtained sorption edges can be reproduced reasonably by the modeling considering single-site cation exchange reactions. Granite is complex mineral assemblages. However, the combined microscopic and macroscopic approaches revealed that elementary reactions by single phase can be representative for the bulk sorption reaction in complex mineral assemblages.
M of Eu(III) and analyzed using EPMA and LA-ICP-MS. The Eu enrichment up to 6 wt.% was observed on most of the biotite grains. The Eu-enriched parts commonly lose K, which is the interlayer cation of biotite, indicating that the sorption mode is cation exchange in the interlayer. Batch Eu(III) sorption experiments on granite and biotite powders were conducted. The macroscopic sorption behavior of biotite was consistent with that of granite. The obtained sorption edges can be reproduced reasonably by the modeling considering single-site cation exchange reactions. Granite is complex mineral assemblages. However, the combined microscopic and macroscopic approaches revealed that elementary reactions by single phase can be representative for the bulk sorption reaction in complex mineral assemblages.
Seki, Miharu*; Oikawa, Junichi*; Taguchi, Taro*; Onuki, Toshihiko; Muramatsu, Yasuyuki*; Sakamoto, Kazunori*; Amachi, Seigo*
Environmental Science & Technology, 47(1), p.390 - 397, 2013/01
Times Cited Count:44 Percentile:75.12(Engineering, Environmental)The laccase released by microorganisms oxidizes iodide to molecular iodine or hypoiodous acid, both of which are easily incorporated into natural soil organic matter.